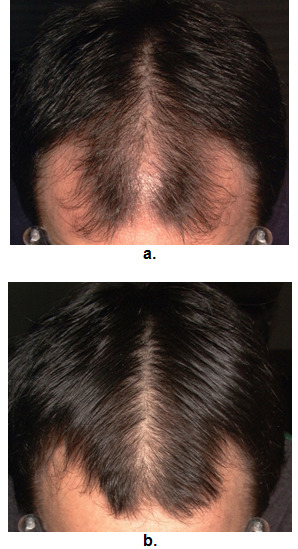
Hair Thinning in Men is a common issue affecting millions of men worldwide. Although often seen as a natural part of aging, hair thinning can begin as early as a man’s 20s or 30s and can have a significant impact on confidence and self-esteem. While genetics is the primary cause for many, other factors, such as hormonal imbalances, stress, lifestyle habits, and nutritional deficiencies, also contribute to hair thinning. This article explores the causes of hair thinning in men, provides data on its prevalence, analyzes the available treatments, and breaks down the associated costs.
Hair Thinning in Men
Hair thinning, particularly male pattern baldness (androgenic alopecia), is one of the most common forms of hair loss. It is characterized by a progressive loss of hair density, often starting at the temples, crown, or hairline and gradually advancing to other areas of the scalp. Unlike hair shedding, which occurs when hair falls out but grows back normally, hair thinning involves a gradual reduction in the size of hair follicles, leading to finer and shorter hair over time.
The hair-thinning process can be divided into the following stages:
- Stage 1: Slight thinning around the temples and hairline.
- Stage 2: Increased thinning at the crown, often referred to as a “bald spot.”
- Stage 3: Noticeable loss of hair at the top of the scalp and receding hairline.
- Stage 4: More advanced thinning leading to larger bald patches on the scalp.
- Stage 5: Complete hair loss or extremely thin hair across large portions of the scalp.
Statistical Data on Hair Thinning in Men
Hair thinning in men is incredibly common and affects millions globally. According to the American Hair Loss Association (AHLA), approximately two-thirds of men will experience some degree of hair thinning by age 35, and 85% of men will have significant thinning by the time they reach age 50. In more severe cases, some men may start to see noticeable thinning in their late teens and early 20s.
Global Prevalence
Hair thinning is a global issue affecting men in different countries and regions:
- In the United States, about 50 million men suffer from some form of hair thinning or hair loss, with the prevalence increasing significantly with age.
- In the United Kingdom, an estimated 8 million men experience some degree of hair thinning.
- In Asia, hair thinning affects about 73% of men at some point in their lives, with rates of male pattern baldness rising sharply after age 40.
Age-Related Prevalence
The likelihood of hair thinning increases with age:
- By age 30: 30% of men will experience hair thinning.
- By age 50: 50% of men will have noticeable thinning or balding.
- By age 70: 80% of men will experience advanced hair loss.
Causes of Hair Thinning in Men
a. Genetics and Androgenic Alopecia
The most common cause of hair thinning in men is androgenic alopecia, also known as male pattern baldness. This condition is largely hereditary and is influenced by hormones, particularly dihydrotestosterone (DHT). DHT is derived from testosterone and binds to hair follicles, causing them to shrink and weaken over time. As a result, the hair follicles produce shorter, finer hairs until they stop producing new hair altogether.
b. Hormonal Imbalances
Aside from DHT, other hormonal imbalances can contribute to hair thinning. For instance, low testosterone levels or thyroid disorders can negatively affect hair growth. Men with conditions like hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism may experience diffuse thinning across the scalp.
c. Nutritional Deficiencies
A lack of essential nutrients can weaken hair follicles and slow down hair growth. Common nutritional deficiencies that contribute to hair thinning in men include:
- Iron: Iron deficiency (anemia) reduces oxygen flow to hair follicles, causing thinning.
- Zinc: Zinc is necessary for tissue repair and hair growth. A deficiency can lead to hair loss.
- Biotin: Biotin (Vitamin B7) is essential for hair health, and a deficiency can cause thinning and brittle hair.
- Protein: As hair is primarily made up of keratin (a type of protein), inadequate protein intake can hinder hair growth.
d. Stress and Telogen Effluvium
Physical or emotional stress can trigger telogen effluvium, a temporary condition where hair enters the shedding phase prematurely. While telogen effluvium is often reversible, it can exacerbate underlying genetic hair thinning if not addressed.
e. Medications
Certain medications have hair thinning listed as a side effect. These include:
- Chemotherapy drugs
- Beta-blockers
- Antidepressants
- Blood pressure medications
Hair Thinning Treatments
Hair thinning in men has given rise to a massive industry offering various treatment options. These treatments range from medications and topical treatments to surgical procedures and non-invasive solutions. Below is an analysis of the most popular hair thinning treatments, their effectiveness, and associated costs.
a. Medications
- Minoxidil (Rogaine) Minoxidil is one of the most widely used over-the-counter treatments for hair thinning. Available as a topical solution or foam, it works by stimulating blood flow to the hair follicles, prolonging the growth phase of hair. Minoxidil is applied directly to the scalp and is used daily for several months to see noticeable results. According to clinical studies, 40% of men see moderate to dense hair regrowth after using minoxidil for three to six months.
- Price: $20 to $50 per month.
- Effectiveness: Moderately effective for early-stage thinning. Continuous use is required to maintain results.
- Finasteride (Propecia) Finasteride is a prescription oral medication that works by inhibiting the conversion of testosterone to DHT, effectively reducing the levels of DHT in the scalp. Finasteride is highly effective in treating male pattern baldness, particularly at the crown and mid-scalp. Clinical studies show that 90% of men taking finasteride see slowed hair thinning, and around 65% experience regrowth within two years.
- Price: $30 to $60 per month.
- Effectiveness: Highly effective for androgenic alopecia. Potential side effects include decreased libido.
- Dutasteride (Avodart) Dutasteride is another DHT blocker similar to finasteride, but it is even more potent. It is primarily used to treat an enlarged prostate but has been shown to effectively slow hair thinning. Due to its stronger effects, it may be prescribed in cases where finasteride is not effective.
- Price: $50 to $100 per month.
- Effectiveness: Highly effective, but not widely prescribed for hair thinning due to its potency.
b. Topical Treatments
- Hair Growth Shampoos Several shampoos claim to reduce hair thinning by nourishing the scalp and hair follicles. Ingredients like ketoconazole, biotin, caffeine, and saw palmetto are commonly found in these products. While shampoos alone are not a solution to male pattern baldness, they can help improve scalp health and support other treatments like minoxidil or finasteride.
- Price: $10 to $40 per bottle.
- Effectiveness: Mildly effective, often used as part of a broader hair care routine.
c. Laser Therapy
Low-Level Laser Therapy (LLLT) is a non-invasive treatment that uses light energy to stimulate hair follicles and encourage hair regrowth. LLLT can be done through in-office treatments or with at-home devices like laser combs or caps. Studies have shown that LLLT can increase hair density by 15% to 20% after several months of use.
- Price: $200 to $900 for at-home devices.
- Effectiveness: Moderately effective, especially when combined with other treatments.
d. Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy
PRP therapy involves drawing a patient’s blood, processing it to concentrate the platelets, and then injecting it into the scalp. Platelets contain growth factors that can stimulate hair follicles and improve hair growth. A study published in 2019 found that PRP treatment resulted in a 30% increase in hair density after three to six months of treatment.
- Price: $500 to $2,000 per session (multiple sessions required).
- Effectiveness: Effective for stimulating new hair growth, but results may take time.
e. Hair Transplant Surgery
So, Hair transplant surgery is a permanent solution for men experiencing advanced hair thinning or balding. Hair follicles are transplanted from areas of dense growth (often the back or sides of the scalp) to thinning or balding areas. The two primary methods are Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT) and Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE).
- Price: $4,000 to $15,000, depending on the extent of the procedure.
- Effectiveness: Highly effective for long-term hair restoration, especially for male pattern baldness.
Non-Surgical and Cosmetic Solutions
- Scalp Micropigmentation (SMP) Scalp micropigmentation is a non-surgical procedure that involves tattooing tiny dots on the scalp to create the illusion of hair follicles and denser hair. This option is purely cosmetic and does not regrow hair, but it can significantly improve the appearance of thinning hair.
- Price: $1,500 to $4,000, depending on the size of the treated area.
- Effectiveness: Cosmetic; effective in creating a fuller appearance.
- Hair Systems (Toupees or Wigs) Hair systems or toupees offer a quick and non-permanent solution for men experiencing significant hair thinning. Modern hairpieces are made from high-quality synthetic or human hair and can be styled to suit personal preferences.
- Price: $200 to $3,000, depending on the material and customization.
- Effectiveness: Aesthetic solution with no impact on hair growth.
Emerging Treatments and Future Trends
As the demand for effective hair thinning treatments grows, ongoing research is focused on developing new solutions. Some promising developments include:
- Stem Cell Therapy: This involves using stem cells to regenerate hair follicles and stimulate new growth. Though still in experimental stages, early results are promising.
- Gene Therapy: Scientists are investigating ways to target the genes responsible for male pattern baldness, potentially offering a permanent solution to genetic hair thinning.
- Exosome Therapy: Exosomes are tiny particles that facilitate communication between cells. In hair restoration, exosome therapy is being explored to stimulate follicle growth and improve hair density.
Treatment Costs: A Comparative Analysis
The cost of treating hair thinning in men can vary significantly depending on the method used. Here’s a comparison of the most common treatments:
| Treatment | Price Range | Effectiveness | Duration of Results |
|---|---|---|---|
| Minoxidil (Rogaine) | $20-$50/month | Moderately effective | Ongoing; requires continuous use |
| Finasteride (Propecia) | $30-$60/month | Highly effective | Ongoing; requires continuous use |
| Laser Therapy (LLLT) | $200-$900 | Moderately effective | Requires multiple treatments |
| PRP Therapy | $500-$2,000/session | Effective | Long-term, but may require maintenance |
| Hair Transplant Surgery | $4,000-$15,000 | Highly effective; permanent solution | Long-term |
| Scalp Micropigmentation | $1,500-$4,000 | Cosmetic; creates appearance of thicker hair | Long-term |
| Hair Systems (Toupees/Wigs) | $200-$3,000 | Aesthetic solution | Ongoing maintenance required |
Conclusion
Hair thinning in men is a widespread issue that affects millions globally, with both genetic and environmental factors playing a role. The good news is that advancements in hair restoration have led to a wide range of treatments, from over-the-counter solutions like minoxidil to surgical options like hair transplants.
The cost of these treatments varies depending on their complexity, but many offer effective ways to combat hair thinning and restore confidence. While some solutions, such as hair transplants, can be expensive, less invasive options like minoxidil or finasteride provide more affordable alternatives